
Internet marketing, search engines, spiders, google updates, SEO. What are they? Why do they matter?
The Internet

The internet (Web) started off as just a network of interconnected of pages which you could only reach by searching for it directly, or via links. Since then the Web had grown too large to use such a simple method.
Search Engines

In response to this, in the early 1990’s, a number of companies (Yahoo, etc) developed search engines where users could type keywords into the search engine and receive a list of websites related to the search phrase, which revolutionized the way that people were using the internet. However (towards the end of the 1990’s), Google distinguished itself from the rest with a search engine that acknowledged links as a signal of authority and trust.
Google is really just a pattern detection program. When you search for a keyword phrase, Google is going to provide you with a list of websites that matches the pattern that’s related to your search. they’re not actually searching the live web. They’re actually searching Google’s index of the web the stored copy of the sites that Google has crawled.
Semrush
Spiders

To populate this index Google uses spiders to crawl the web. They start on a page and check out all the content on that page, and then it follows the links on that page and looks at the content on those pages of which a copy is stored on Google’s servers in Google’s index, in such a way that it can be quickly searched and using its now famous algorithm, rank the pages based on relevancy influenced by a few hundreds of factors. Over the past 2 decades Google has been continually refining its search engine (see figure 1) and a time line of some of the notable updates are recorded below:
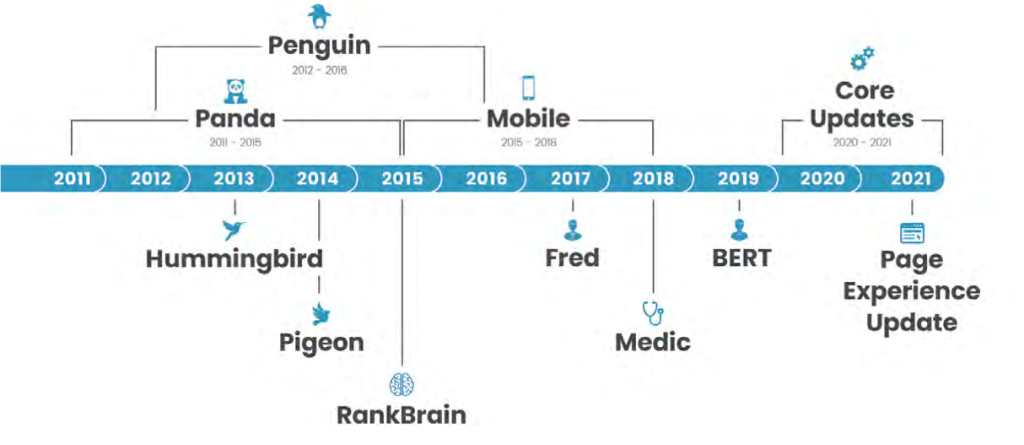
Time line of major Google Algorithm Updates

Google Toolbar (2000)
allowed users to search for information from any page on the Internet,

PandaUpdate (2011)
focused largely on websites providing quality content for users and lower the rankings of low-quality websites

Penguin Update (2012)
penalize websites that were using or buying spammy links

In-depth Articles (2013)
a new set of search results to help users find in-depth, high-quality-articles and rank accordingly.

Hummingbird (2013)
instead of relying only on keyword matching to provide results, the search engine was able to take user search intent into consideration to provide even better results. .. better answer longer and more complex search queries that are phrased in natural language. It shifted many marketers’ priorities to focus on long-tail keywords as well as the quality and context of the content on their sites.

The Mobile Update (2015)
rankings started to depend on a specific page’s mobile-friendliness.

RankBrain Update (2015)
The addition of machine learning and artificial intelligence into Google’s algorithm. the search engine had the ability to better guess what a user was searching for if it was a term Google was originally unfamiliar with.

Mobile Speed Update (2018)
User experience on mobile devices

Page Experience Update
User experience

Spam Update (2021)
Reducing spam
SEO

Click here to find out more about Vibe Marketing East Coast, or here to speak to one of the Vibe Marketing team.

